
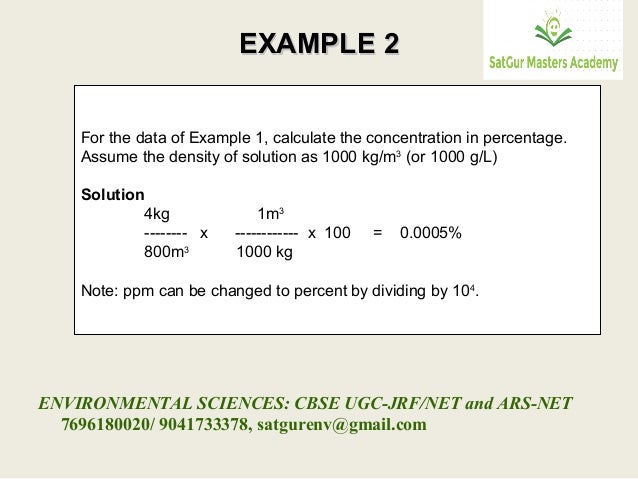
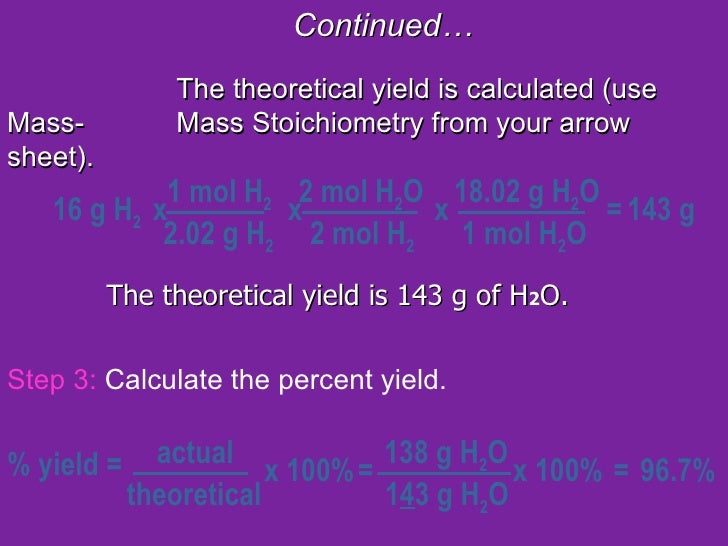
In this example, we will be finding the percentage yield of silver iodide formed by precipitation.ġ0 cm 3 of 1 mol/dm 3 silver nitrate solution was added to an excess of potassium iodide solution. Worked example: calculating the percentage yield of salt preparation Gaseous volume (usually for gas products)Ĥ.Here, the actual and theoretical yields could be expressed in: Percentage yield = actual yield ÷ theoretical yield × 100% The percentage yield is the ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield expressed as a percentage: (37 g/100 g) × 100% = 37%.The theoretical yield of 100 g is the calculated amount of product, assuming that the reaction is 100% efficient.The actual yield of 37 g is the amount of product that is weighed at the end of a reaction.To say this in a cheem manner appropriate for the O Level: This means that you only get 37 g of product in the lab, even though you have put in enough reactants to make 100 g of it. Step 2 is a stumbling block, with the lowest percentage yield of 37%. The example above shows a three-step method to synthesise Lacosamide, an important medication for epilepsy. When you look up cheem research papers, the percentage yield of each reaction is written above the arrow.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
